Get a FREE
ENU Intro Pack*
*Just Pay $2.00 Shipping

What Are the Direct Consequences of Sarcopenia?
As a medical term, many people are familiar with sarcopenia – a Greek term meaning “poverty of the flesh.” However, whether they know it or not, most people are familiar with the effects of this condition, which affects the body’s muscle mass and a person’s physical strength. In fact, virtually everyone will experience the consequences of sarcopenia as they age, making it important for people to at least be aware of what this condition can do and how to best deal with its symptoms. So, what are the direct consequences of sarcopenia, and what can you do to treat or mitigate those effects? To find out, keep reading as the team at ENU, makers of protein shakes for seniors, discuss this topic in greater detail.
The Direct Effects of Sarcopenia
As with many health conditions affecting seniors, the direct consequences of sarcopenia extend well beyond the symptoms of the condition itself – symptoms that include a reduction in the size and number of muscle fibers in the body and a loss of overall strength and power. While people can begin losing muscle mass as early as age 30, they tend to do so at a rate of about 3 to 5% per decade, which can increase to as much as 15% per decade – or more than 1% per year – by the age of 70. As these effects accumulate in the body, those with sarcopenia often find themselves unable to move around and maintain their independence to the degree they’d like. That’s because of the secondary effects of sarcopenia (those caused by the symptoms of the condition), which can lead to a variety of specific consequences, including the following:
Increased Risk of Falls
It’s no secret that falls are among the greatest dangers to seniors, as they can cause life-altering fractures and other injuries that take months to heal; as the muscles in the body weaken due to sarcopenia, those with the condition face an ever-increasing risk of falling, since this reduction in physical strength can affect a person’s balance and ability to catch themselves after a misstep. This increased risk of injury also forces many seniors to move more slowly and carefully, changing how they go about their lives.
Changes to Gait
Though most of us don’t consciously think about our gait – the way in which we walk – it’s undeniable that this trait is part of what defines us as individuals. Whether you step gracefully or clumsily, quickly or slowly, depends on a number of factors, including the strength of your muscles and the ease with which you use them; as sarcopenia sets in, however, your ability to move around is diminished, and your gait can change as a direct consequence. This could manifest as a shuffling gait, a slow walking pace, or a need for support as you walk, but however it looks, sarcopenia is likely a major factor.
Reduction in Physical Activities
Once a person’s arms and legs start to struggle with even the most basic tasks, it’s understandable why they might opt to avoid most forms of exercise. If you were once an avid golfer, for instance, your trips to the local course could become less and less frequent as your ability to walk nine or 18 holes starts to wane, and those who once went on long walks or jogs with friends may find that these meetings in motion are suddenly too taxing to tolerate. Unfortunately, this direct consequence of sarcopenia carries a two-fold risk: It limits a person’s ability to exercise, and, in doing so, deprives them of their best option to slow or stop sarcopenia’s advance.
How to Treat the Direct Consequences of Sarcopenia
Given the many ways in which sarcopenia can diminish a person’s quality of life, you’re probably wondering what you can do to fight the onset of this condition. Luckily, you have a few options that are readily accessible and which can be implemented at any time.
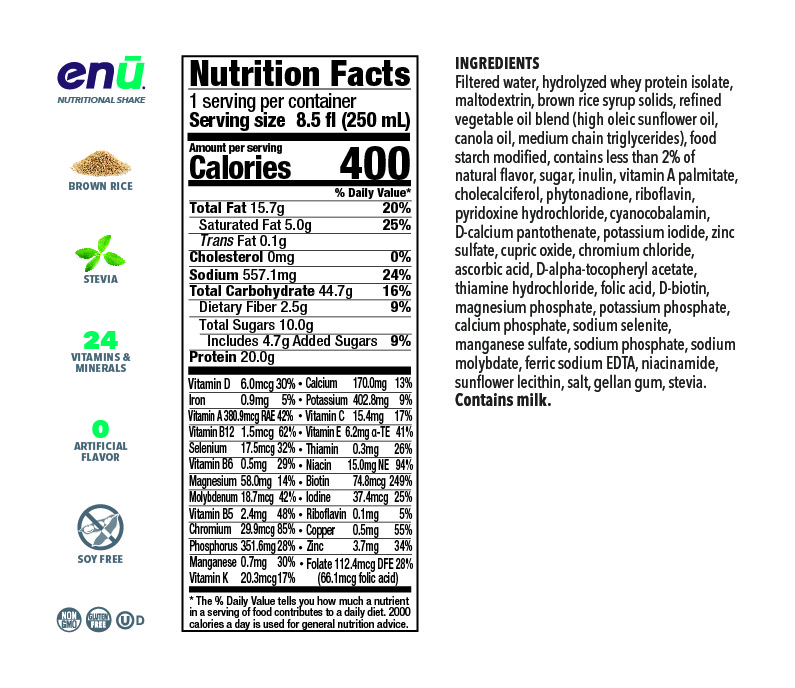
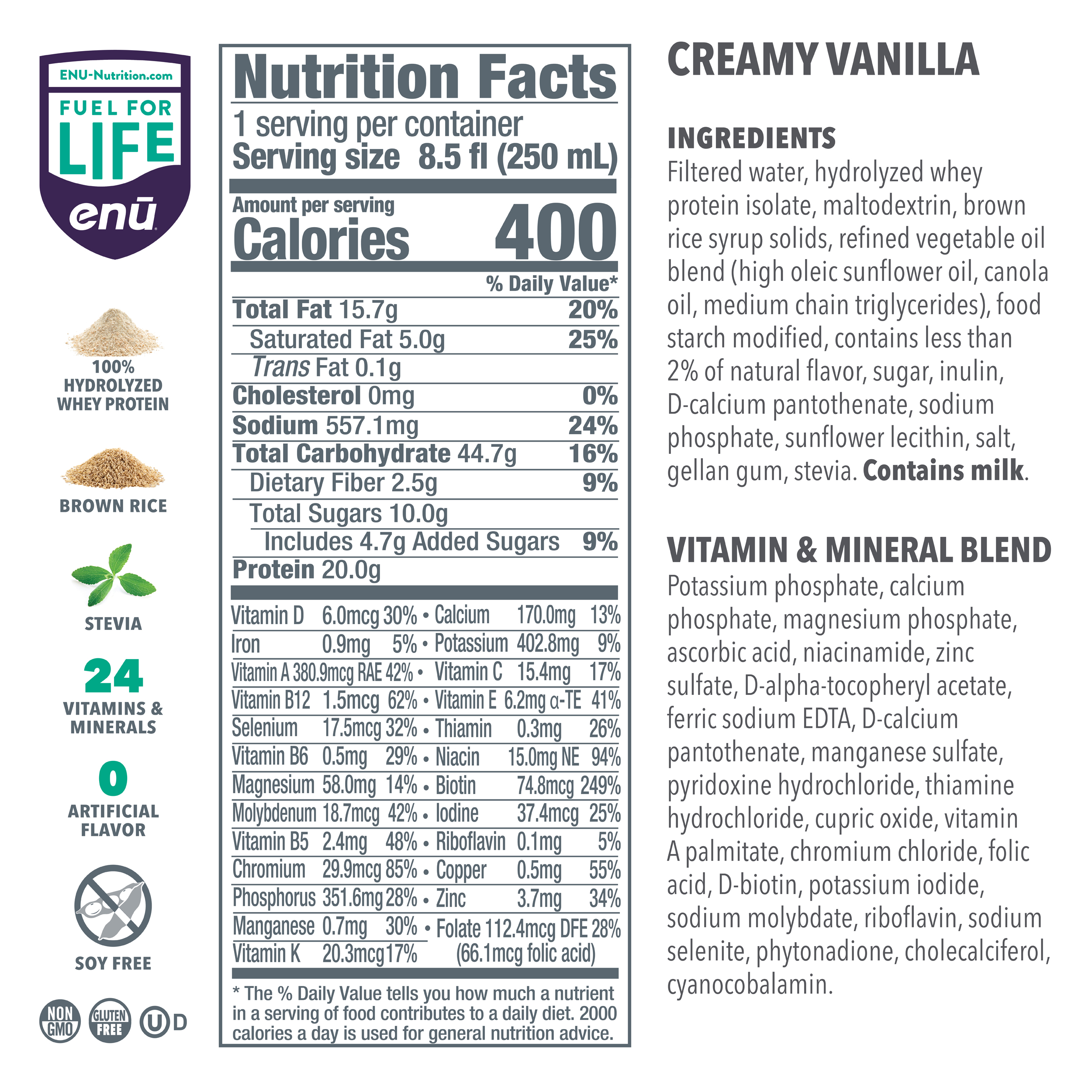
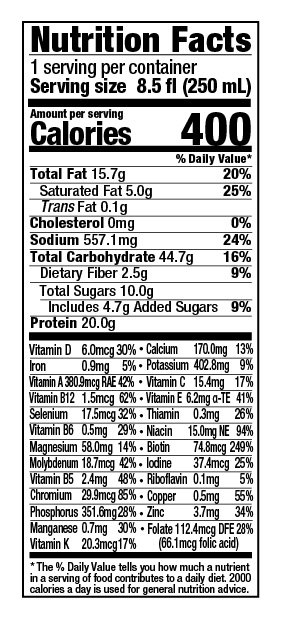
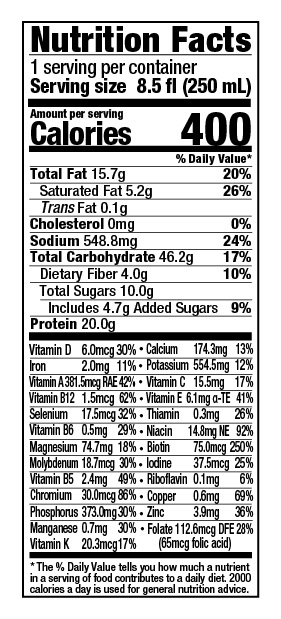
The two chief concerns of those dealing with the consequences of sarcopenia should be diet and exercise. When choosing foods for your diet each day, it’s important that you incorporate plenty of protein, as the amino acids it contains are essential to preserving muscle mass; they also serve as the building blocks of new muscle proteins. Experts recommend a daily intake of at least 1 gram of protein per kilogram of body weight, which translates to about 68 grams of protein for a 150-lb person. To figure out how much protein you should be getting, simply divide your weight in pounds by 2.2 to get your intake in grams per day.
The second concern, exercise, can be a bit trickier to implement for those with sarcopenia, as their increased risk of falling and injuring themselves can make unsupervised exercise a dangerous thing. That said, working out in some form is necessary to build new muscle, so talk to your doctor about a routine that’s safe for you. Another option is to enlist the assistance of a personal trainer or physical therapist who can help you come up with an exercise regimen. Either way, just remember that you need a combination of diet and exercise to ward off the consequences of sarcopenia and strengthen your body overall.
Nutritional Support for Dealing with the Direct Consequences of Sarcopenia
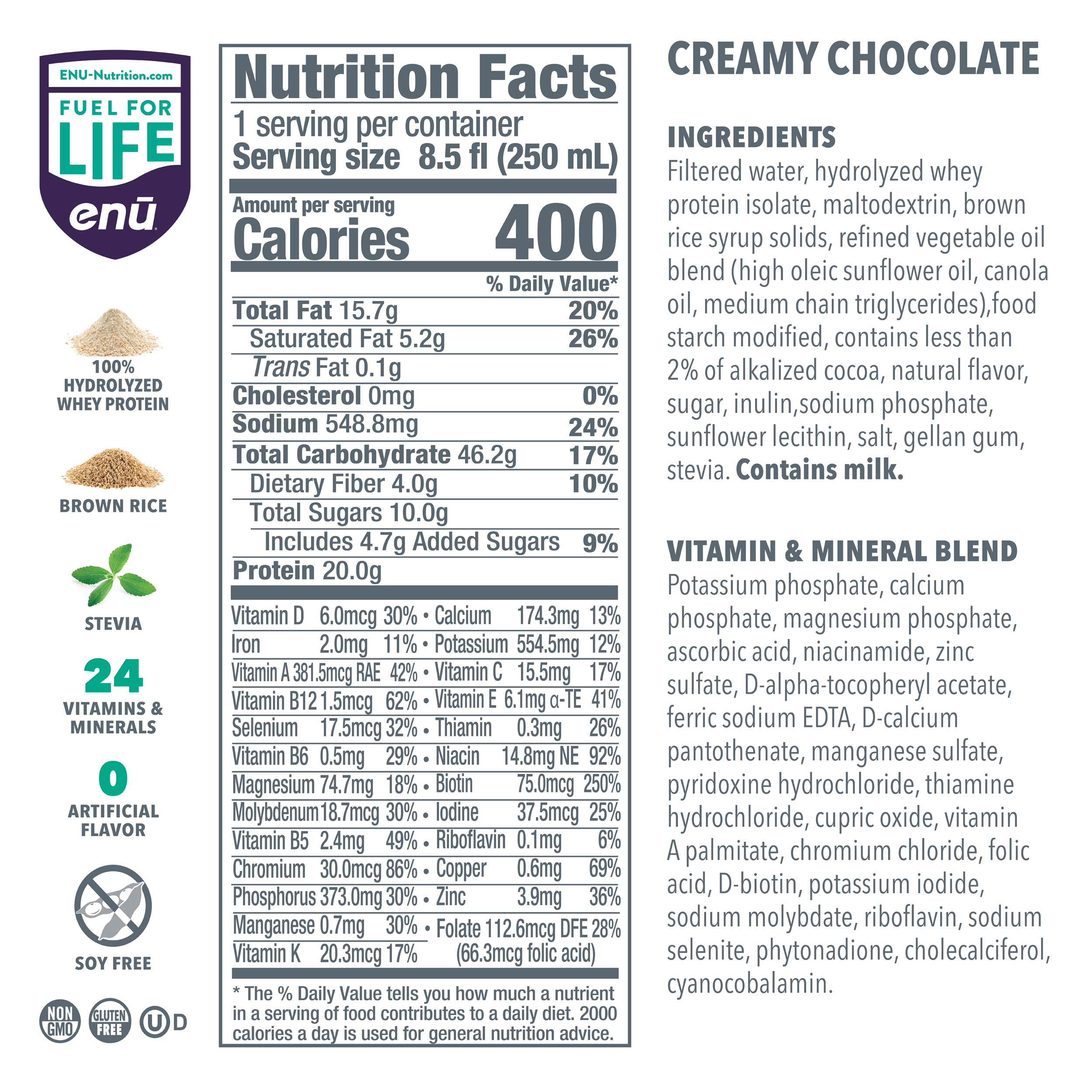
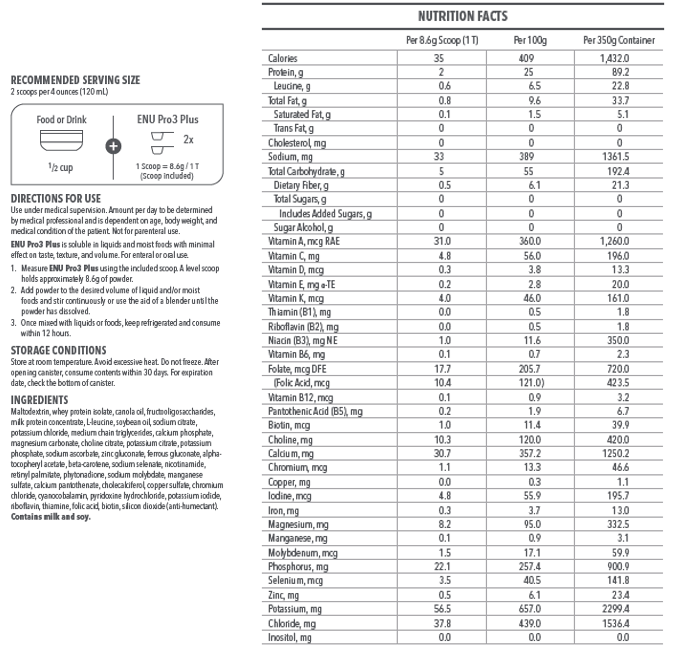
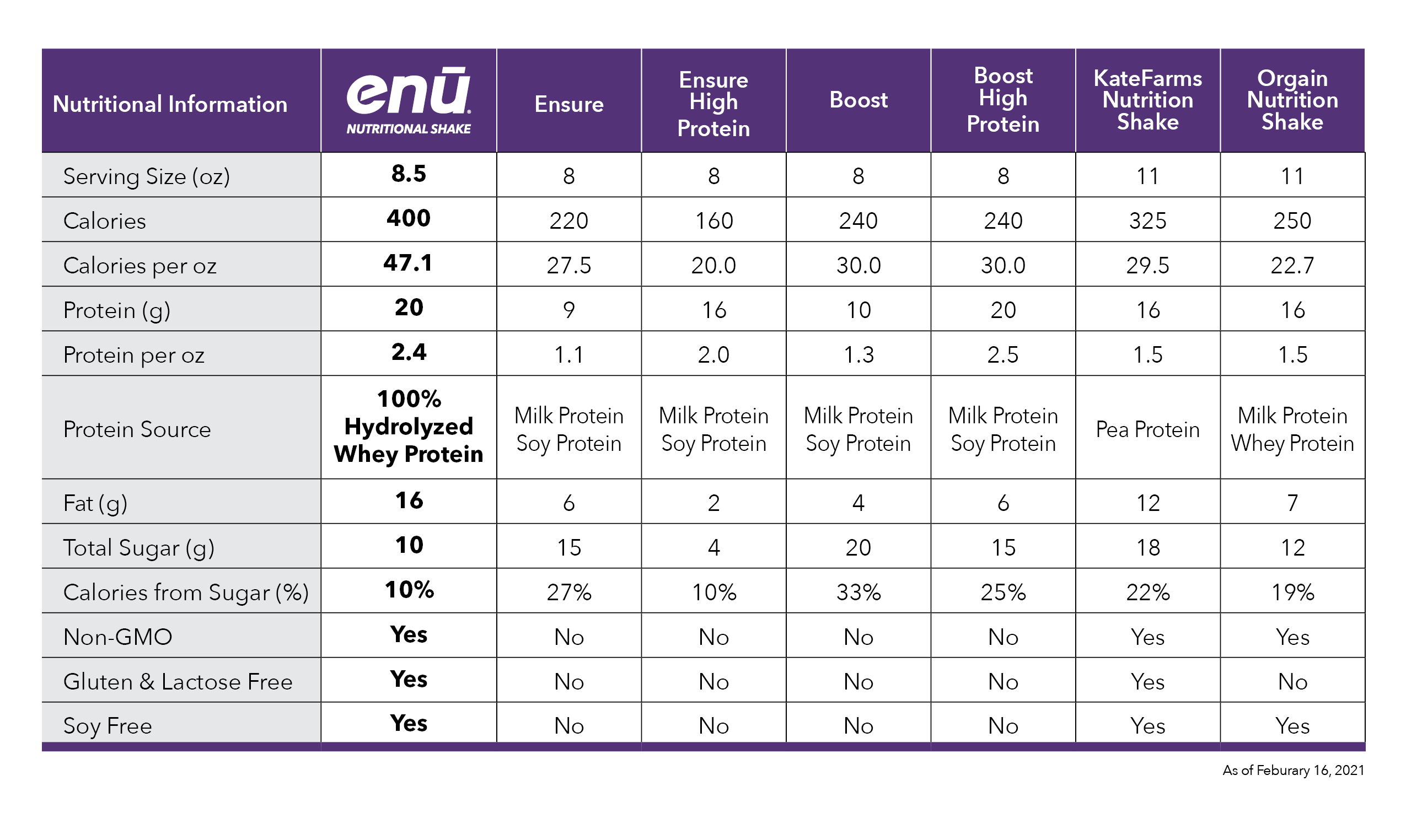
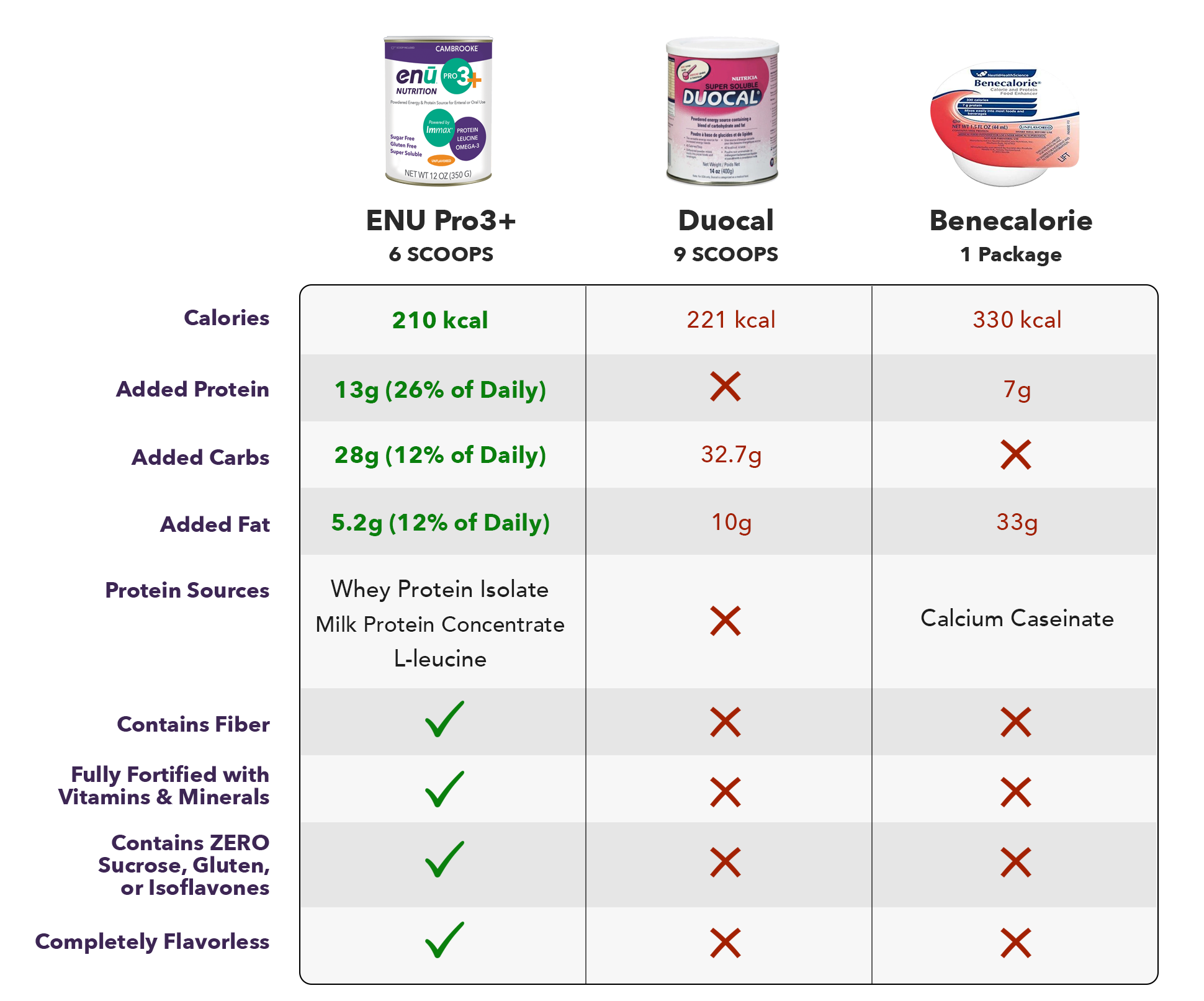
Although getting lots of protein sounds like a simple solution to sarcopenia, implementing this dietary change can be easier said than done. To simplify the process, ENU offers well-rounded meal replacement shakes and powdered nutritional supplements rich in protein, vitamins, and calories – all essential components in anyone’s diet, but especially for those with sarcopenia. To learn more about the benefits of ENU products for you or a loved one, visit us online or call us today at (855) 266-6733.